How to Get White Blood Cells Normal Again
Overview
What are white claret cells?
White blood cells, as well known as leukocytes, are responsible for protecting your body from infection. Equally office of your immune arrangement, white claret cells broadcast in your claret and respond to injury or illness.
Function
What do white claret cells exercise?
White blood cells protect your trunk confronting infection. As your white claret cells travel through your bloodstream and tissues, they locate the site of an infection and deed as an army general to notify other white blood cells of their location to assist defend your trunk from an attack of an unknown organism. In one case your white blood prison cell army arrives, they fight the invader by producing antibody proteins to attach to the organism and destroy information technology.
Anatomy
Where are white claret cells located?
Your white blood cells are in your bloodstream and travel through blood vessel walls and tissues to locate the site of an infection.
What do white claret cells look like?
Contrary to their proper name, white claret cells are colorless just can announced as a very calorie-free purple to pink color when examined under a microscope and colored with dye. These extremely tiny cells take a round shape with a distinct center membrane (nucleus).
How big are white blood cells?
You tin but see white blood cells under a microscope, equally they are extremely pocket-size.
How many white claret cells are in my torso?
White blood cells business relationship for one% of your blood. In that location are more red blood cells in your torso than white claret cells.
How are white blood cells formed?
White claret cell germination occurs in the soft tissue within of your basic (bone marrow). Two types of white claret cells (lymphocytes) grow in the thymus gland (T cells) and lymph nodes and spleen (B cells).
What are white claret cells fabricated of?
White blood cells originate from cells that morph into other cells in the body (stem jail cell) within the soft tissue of your bones (bone marrow).
What are the types of white claret cells?
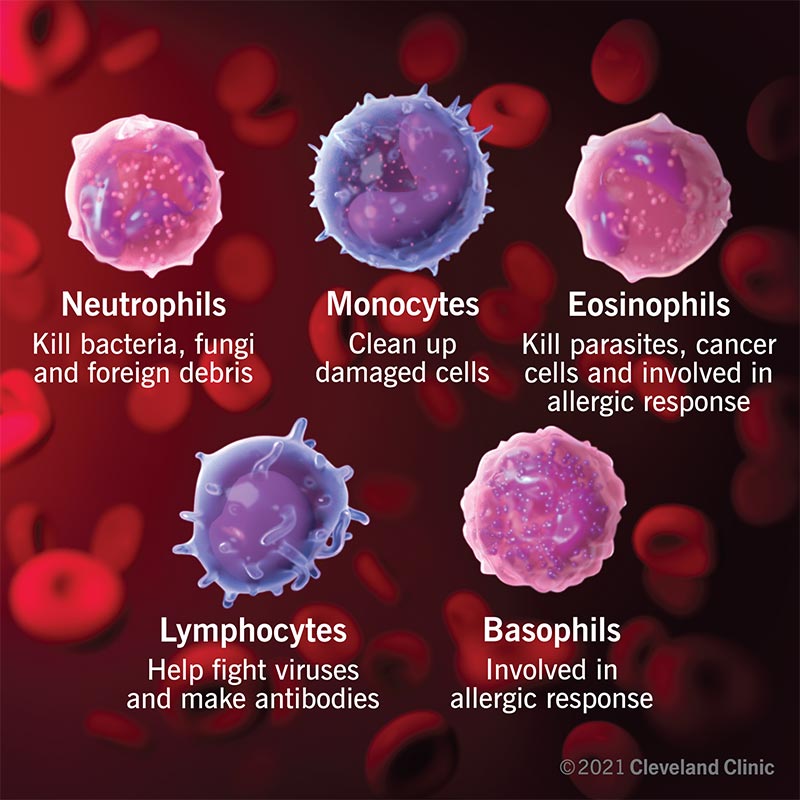
In that location are five types of white claret cells:
- Neutrophils: Help protect your body from infections by killing leaner, fungi and foreign debris.
- Lymphocytes: Consist of T cells, natural killer cells and B cells to protect against viral infections and produce proteins to help you fight infection (antibodies).
- Eosinophils: Identify and destroy parasites, cancer cells and assists basophils with your allergic response.
- Basophils: Produces an allergic response like coughing, sneezing or a runny nose.
- Monocytes: Defend confronting infection by cleaning up damaged cells.
Conditions and Disorders
What are the common conditions and disorders that affect white blood cells?
If yous have a depression white blood cell count, you lot are likely to get infections (leukopenia). If your white blood cell count is likewise high (leukocytosis), y'all may take an infection or an underlying medical condition similar leukemia, lymphoma or an immune disorder.
What are common signs or symptoms of white claret cell conditions?
Symptoms of white blood cell atmospheric condition, where you may have a count that is too loftier or too low include:
- Fever, body aches and chills.
- Wound that is red, swollen, oozes pus or won't heal.
- Frequent infections.
- Persistent cough or difficulty animate.
What is a normal white blood prison cell count?
Information technology is normal for you to produce nearly 100 billion white claret cells each mean solar day. Subsequently completing a blood draw, a exam counts your white blood cells, which equals number of cells per microliter of blood. The normal white claret cell count ranges between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter.
What are common tests to bank check the number of white claret cells?
A complete claret count (CBC) test identifies information about the cells in your claret. A lab completes this test after a medical professional draws your blood and examines your white and red blood cell count.
White blood cells scan is a test to observe infection or abscesses in your body'due south soft tissues. This test involves withdrawing your blood, separating the white blood cells from the sample, tagging them with a radioactive isotope, returning those white blood cells back into your trunk, then an imaging test will place areas that evidence infection or abscess on your body.
What causes a low white blood jail cell count?
Causes of low white claret jail cell count include:
- Os marrow failure (aplastic anemia).
- Os marrow attacked by cancer cells (leukemia).
- Drug exposure (chemotherapy).
- Vitamin deficiency (B12).
- HIV/AIDS.
A blood test with fewer than four,000 cells per microliter of blood diagnoses low white blood cells.
What causes a loftier white blood prison cell count?
Causes of loftier white blood jail cell count include:
- Autoimmune disorders (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Viral infections (tuberculosis, mononucleosis).
- Bacterial infections (sepsis).
- Concrete injury or stress.
- Leukemia or Hodgkins disease.
- Allergies.
A claret examination with more than than 11,000 cells per microliter of blood diagnoses high white blood cells.
What are common treatments for white blood cell disorders?
Treatment for white claret cell disorders vary based on the diagnosis and severity of the condition. Treatment ranges from:
- Taking vitamins.
- Taking antibiotics.
- Surgery to replace or repair bone marrow.
- Claret transfusion.
- Stem cell transplant.
Care
How do I accept care of my white claret cells?
You tin take intendance of your white claret cells by:
- Practicing good hygiene to prevent infection.
- Taking vitamins to heave your immune system.
- Treating medical weather condition where white blood cell disorders are a side event.
A annotation from Cleveland Clinic
White claret cells serve equally your first line of defense confronting injury or illness. Keep your white claret cells salubrious by taking vitamins to heave your immune organization and practicing practiced hygiene to foreclose infection. If you feel whatever symptoms like fever and chills, frequent infection, persistent cough or difficulty breathing, contact your healthcare provider to test if your white blood cell count is aberrant.
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21871-white-blood-cells